Top Food Business Ideas for 2025 | Start Your Culinary Venture


Discover nine trending food business concepts for 2025, from food trucks to online cooking classes. Learn the pros, cons, startup costs and expert tips for launching your culinary venture.
Top Food Business Ideas for 2025 | Start Your Culinary Venture
Hungry for Success? Launch Your Dream Food Business
Looking for profitable food business ideas? This listicle serves up nine trending concepts for 2025, from food trucks to online cooking classes. Discover the pros, cons, startup costs, and potential break-even timelines for each idea. We'll explore examples and expert tips for launching ventures like artisanal bakeries, plant-based food product lines, and specialty food e-commerce. Find the perfect food business idea to turn your culinary passion into a thriving enterprise.
1. Food Truck Business
Looking for exciting food business ideas? The food truck business model offers a unique blend of culinary creativity and entrepreneurial spirit. It involves selling prepared food from a mobile vehicle, equipped with a kitchen, allowing you to bring your delicious creations directly to your customers. This approach provides flexibility in location and menu offerings, and often comes with significantly lower startup costs than a traditional restaurant. Food trucks can target diverse markets, from bustling urban centers and lively events to vibrant festivals and busy business districts. This makes it a particularly appealing option for those seeking accessible entry points into the food industry.
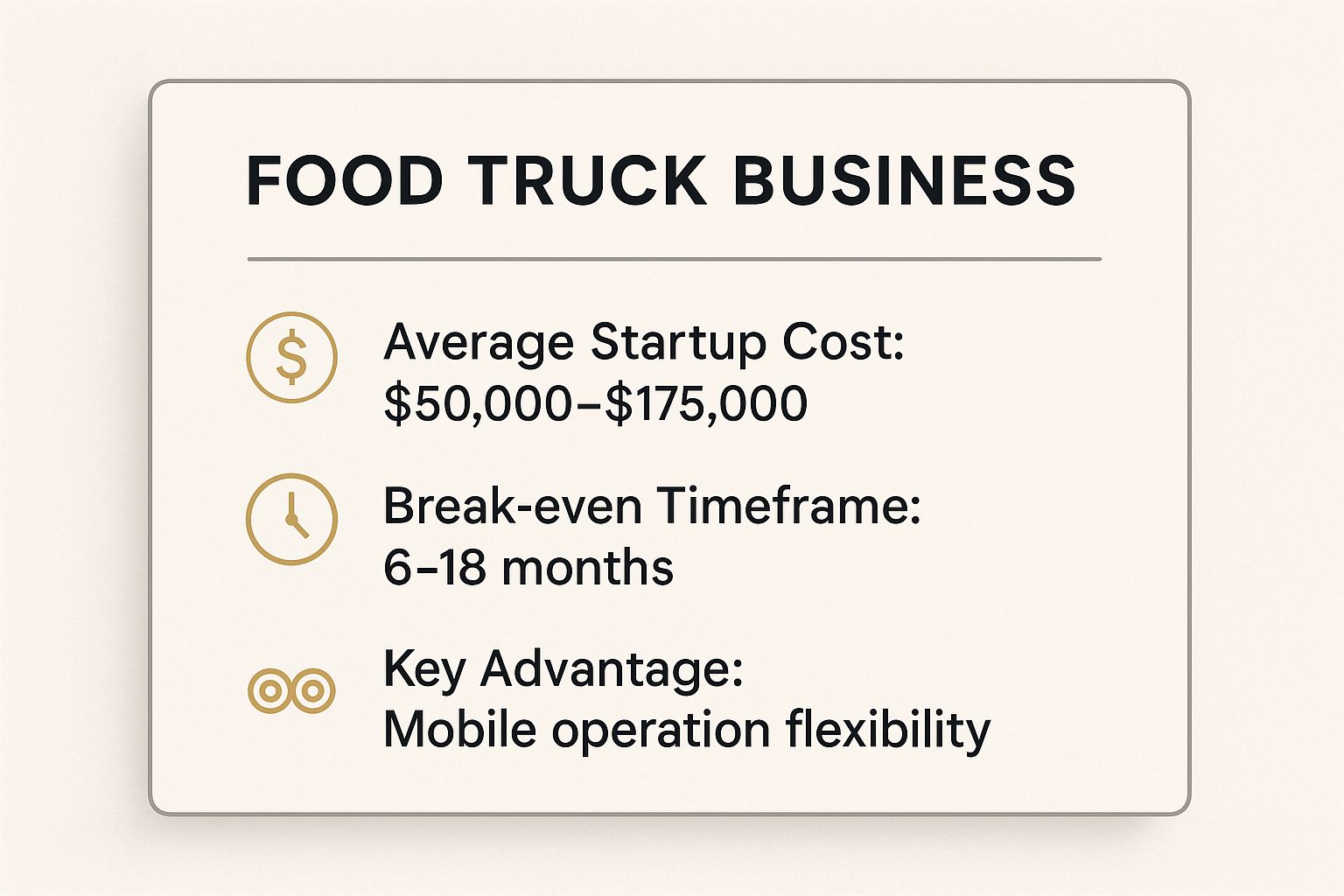
The infographic above visualizes key data points about starting a food truck business, highlighting the startup costs, potential revenue, and key operational aspects. This quick reference underscores the potential profitability and emphasizes the importance of strategic planning.
Here's a summary of key takeaways from the infographic:
- Startup Costs: Typically range from $50,000 - $175,000, significantly less than a brick-and-mortar restaurant.
- Potential Revenue: Can generate substantial income, with successful trucks often exceeding $500,000 annually.
- Key Operations: Emphasizes crucial aspects like securing permits, menu planning, marketing, and efficient operations.
As you can see, the potential for success is significant, but careful planning is essential. Now, let's dive into the specifics. The food truck model is attractive due to its mobile operation, enabling you to change locations based on demand, and its lower overhead compared to traditional restaurants. This mobility also allows you to test different concepts and menus before scaling, tailoring your offerings to specific audiences and events. A customizable menu and specialization options, such as focusing on a specific cuisine or dietary niche, can help establish a strong brand identity. Furthermore, social media plays a pivotal role in marketing, allowing food trucks to announce their locations, engage with customers, and build a loyal following.
Pros:
- Lower initial investment: Typically between $50,000 and $175,000.
- Reduced overhead costs: No expensive restaurant lease or large utility bills.
- Flexibility to follow customer demand: Go where the hungry crowds are!
- Ability to build a brand before expanding: Test the market and build a following.
- Creative freedom with menu concepts: Experiment and develop unique offerings.
Cons:
- Regulatory challenges with permits and licenses: Navigating local regulations can be complex.
- Weather dependency: Rain or extreme temperatures can impact sales.
- Limited space for food preparation: Requires efficient workflow and menu planning.
- Mechanical maintenance costs: Truck repairs and upkeep can be unexpected expenses.
- Seasonal fluctuations in business: Depending on your location, winter months might see a dip in sales.
Examples of Successful Food Truck Businesses:
- Kogi BBQ (Los Angeles): Pioneered the gourmet food truck movement with its Korean-Mexican fusion cuisine.
- The Halal Guys (New York): Started as a humble food cart and expanded into a global franchise.
- Curry Up Now (San Francisco): Elevated Indian street food and expanded to multiple locations.
Tips for Starting a Food Truck Business:
- Research local regulations and required permits thoroughly: This is crucial for legal operation.
- Focus on a specific cuisine or signature dish: Stand out from the competition with a unique offering.
- Develop a strong social media presence to announce locations: Engage with customers and build a following.
- Consider joining food truck associations for networking: Learn from others and gain valuable insights.
- Start with a simple, focused menu that can be prepared efficiently: Streamline operations in the limited space.
Popularized By:
Roy Choi (Kogi BBQ), Food Network shows like 'The Great Food Truck Race', and Jon Favreau's film 'Chef' all contributed to the rising popularity of food trucks.
The food truck business deserves its place on this list of food business ideas because it offers a lower barrier to entry, greater flexibility, and the potential for significant growth. It's an ideal choice for aspiring food entrepreneurs looking to test the waters and establish their culinary brand.
2. Meal Prep Service
Looking for food business ideas? A meal prep service is a fantastic option, especially if you're passionate about health and convenience. This business model revolves around preparing and delivering ready-to-eat or ready-to-heat meals directly to customers. It caters to a growing market of busy professionals, health-conscious individuals, and those with specific dietary needs who want nutritious meals without the hassle of grocery shopping and cooking. This makes it a worthy contender among other food business ideas.
Here's how it works: Customers typically subscribe to a weekly or monthly plan, choosing from a rotating menu of dishes. Customization is often a key feature, allowing customers to select meals based on their dietary preferences (keto, vegan, paleo, etc.), calorie goals, or allergies. Prepared meals are then packaged and delivered to their doorstep, ready to be enjoyed.
The success of companies like Freshly (acquired by Nestlé for $1.5 billion) and Factor75 (acquired by HelloFresh) demonstrates the viability and profitability of this business model. Trifecta Nutrition, another prominent example, carved a niche by specializing in organic meal delivery. These examples highlight the potential to scale and even attract significant investment.
Why Choose a Meal Prep Service as a Business Idea?
This business model aligns perfectly with current health and wellness trends, making it an attractive option for today's consumers. The subscription model provides a predictable revenue stream, while the ability to specialize in specific diets allows for targeted marketing and caters to a niche audience. You can even start small from a home kitchen in many jurisdictions (always check local regulations) before expanding to a larger commercial facility. Learn more about Meal Prep Service for low-investment options to get started.
Features and Benefits:
- Subscription-based model: Creates recurring revenue and simplifies forecasting.
- Customizable meal plans: Caters to diverse dietary needs and preferences.
- Focus on health and nutrition: Appeals to a health-conscious market segment.
- Professional packaging and delivery systems: Ensures food safety and quality.
- Menu rotation: Keeps customers engaged and prevents menu fatigue.
Pros:
- Recurring revenue through subscriptions
- Potential to start small from a home kitchen
- Scalable business model
- Alignment with health and wellness trends
- Niche specialization opportunities
Cons:
- Food safety and handling regulations can be complex
- Short shelf life of products necessitates efficient logistics
- Delivery logistics can be challenging
- Customer acquisition costs can be high
- Menu fatigue requires constant innovation
Tips for Success:
- Start with a niche: Focusing on a specific dietary need (e.g., vegan, gluten-free) can differentiate your business.
- Invest in quality packaging: Maintain food freshness and enhance presentation.
- Provide clear nutritional information: Transparency builds trust and caters to informed consumers.
- Develop efficient production processes: Optimize workflows to maintain profit margins.
- Build relationships with local suppliers: Source high-quality ingredients consistently.
Meal prep services have been popularized by figures like Michael Wystrach (Freshly co-founder) and numerous fitness influencers promoting the convenience and health benefits. Even celebrity chefs are entering the prepared meal space, further validating the market's potential. If you're seeking food business ideas that tap into a growing market and offer scalability, a meal prep service could be the perfect fit.
3. Specialty Coffee Shop
Looking for food business ideas with a loyal following and high profit potential? A specialty coffee shop might be the perfect brew. This business model focuses on providing a high-quality coffee experience, emphasizing carefully sourced beans, precise brewing methods, and a curated atmosphere. It's more than just a caffeine fix; it's about savoring the nuances of each cup and immersing oneself in coffee culture. These shops cater to a growing consumer demand for artisanal and handcrafted beverages, making it a compelling option among various food business ideas.

Specialty coffee shops distinguish themselves through several key features. They often source beans directly from farmers or through ethical trading practices, ensuring high quality and supporting sustainable agriculture. Specialized brewing equipment, like pour-over devices and espresso machines, allows baristas to extract the best flavors from each bean. Highly trained baristas with deep product knowledge guide customers through the menu, explaining the origins and tasting notes of different coffees. Finally, the atmosphere of a specialty coffee shop is carefully designed to enhance the customer experience, encouraging patrons to relax, socialize, and appreciate the craft of coffee.
Examples of successful specialty coffee shops include:
- Blue Bottle Coffee: Known for its meticulous approach to sourcing and brewing, Blue Bottle has become a major player in the specialty coffee market.
- Intelligentsia Coffee: This Chicago-based roaster and retailer focuses on direct trade relationships with farmers and a commitment to quality.
- Stumptown Coffee Roasters: Originating in Portland, Stumptown has built a reputation for its expertly roasted beans and skilled baristas.
Pros:
- High profit margins: Specialty drinks command premium prices.
- Loyal customer base: The focus on quality and experience fosters community.
- Complementary product opportunities: Selling beans, brewing equipment, and pastries increases revenue streams.
- Less complex food preparation: Compared to full-service restaurants, the food offerings are typically simpler.
- Strong cultural trend: Artisanal and handcrafted products are in high demand.
Cons:
- High competition: Urban markets can be saturated with coffee shops.
- Significant initial equipment investment: Specialized brewing equipment can be costly.
- Staff training requirements: Investing in barista training is essential.
- Price sensitivity: Some consumers may be resistant to higher prices.
- Dependency on skilled labor: Maintaining consistent quality relies on experienced baristas.
Tips for Success:
- Invest in staff education: Train your baristas on coffee origins, brewing techniques, and customer service.
- Create a distinctive atmosphere: Design a space that reflects your brand and encourages customers to linger.
- Consider vertical integration: Roasting your own beans can increase control over quality and potentially boost profits.
- Partner with local bakeries: Offering fresh pastries and other complementary food items enhances the customer experience.
- Invest in water filtration: Water quality significantly impacts coffee flavor.
When to consider this approach:
This is an ideal food business idea if you are passionate about coffee and dedicated to providing a high-quality product and experience. If you are willing to invest in training, equipment, and creating a unique brand, a specialty coffee shop can be a rewarding and profitable venture. This approach is particularly well-suited to urban areas with a thriving coffee culture and a customer base that appreciates artisanal products. It's a strong contender amongst food business ideas, especially given the enduring popularity of coffee and the growing appreciation for quality brews.
4. Virtual Kitchen/Ghost Restaurant
Looking for innovative food business ideas? A virtual kitchen, also known as a ghost restaurant or cloud kitchen, might be the perfect fit. This delivery-only model is revolutionizing the food industry, offering a streamlined and cost-effective approach to food service. Essentially, a virtual kitchen prepares food in a commercial kitchen space solely for delivery, eliminating the need for a traditional dine-in area. This allows entrepreneurs to tap into the growing demand for food delivery without the overhead of a brick-and-mortar establishment.
How it Works: Virtual kitchens operate by partnering with third-party delivery apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub, or by utilizing their own proprietary ordering systems. Orders are received digitally, prepared in the kitchen, and then picked up by delivery drivers for transport to customers. This model allows for significant flexibility, as multiple brands or cuisine concepts can be operated from a single kitchen.
Examples of Success: The virtual kitchen model has seen tremendous growth, with companies like CloudKitchens (founded by former Uber CEO Travis Kalanick), Virtual Dining Concepts (behind brands like MrBeast Burger and Pauly D's Italian Subs), and Rebel Foods (operating over 45 brands internationally) leading the charge. These examples demonstrate the scalability and profitability potential of this business model.
Why Choose a Virtual Kitchen?
This approach is ideal for aspiring food entrepreneurs seeking lower startup costs and increased operational flexibility. It's a particularly attractive option in today's market, with the rise in food delivery demand and the increasing costs of traditional restaurant spaces. This business model deserves its place on any list of food business ideas because it allows for rapid testing and iteration of different menu concepts without the significant financial risk associated with opening a full-scale restaurant.
Features and Benefits:
- Delivery-only business model: Focus solely on delivery, streamlining operations.
- Multiple brands, one kitchen: Maximize kitchen utilization and cater to diverse customer preferences.
- Reduced real estate footprint and costs: Operate from smaller, less expensive kitchen spaces, often in industrial areas.
- Data-driven menu optimization: Leverage delivery platform data to refine menus based on customer demand and preferences.
- Integration with delivery platforms: Seamlessly connect with existing delivery networks for broad reach.
Pros & Cons:
Pros:
- Lower startup and operational costs.
- Flexibility to pivot menu concepts quickly.
- Ability to test multiple brands simultaneously.
- Reduced staffing needs (no front-of-house staff).
- Location flexibility.
Cons:
- Dependency on delivery platforms and their associated fees.
- Challenges in building brand recognition in a crowded digital marketplace.
- Limited customer interaction and direct feedback.
- Maintaining food quality and packaging integrity during delivery can be challenging.
- Competitive digital marketplace requires strong marketing efforts.
Actionable Tips for Success:
- Optimize packaging: Invest in quality packaging that maintains food temperature and prevents spills during transit.
- Strong digital branding: Create a compelling online presence and distinct brand identity to stand out on delivery platforms.
- Data analysis: Utilize data from delivery platforms to optimize menus and pricing strategies.
- Multiple cuisine concepts: Consider offering different cuisines to maximize kitchen usage and appeal to a wider audience.
- Delivery-friendly food: Focus on menu items that travel well and maintain their quality during delivery.
Learn more about Virtual Kitchen/Ghost Restaurant
The virtual kitchen model is an exciting and innovative approach to the food business, particularly for those seeking a more agile and cost-effective entry point. By focusing on delivery optimization, data-driven decision making, and strong digital branding, virtual kitchen entrepreneurs can carve out a successful niche in the evolving food industry. This method is particularly relevant for today's entrepreneurs, offering a modern solution to the challenges of traditional restaurant ownership.
5. Artisanal Bakery
Looking for food business ideas that tap into a growing market craving quality and authenticity? An artisanal bakery could be your perfect recipe for success. This business model focuses on crafting high-quality, handcrafted bread and pastries using traditional methods and premium ingredients. Forget mass-produced loaves; artisanal baking emphasizes the art of fermentation, hand-shaping, and often incorporates local or organic ingredients to create truly distinctive products. This approach fosters a connection to the craft and results in baked goods bursting with flavor and character.

Artisanal bakeries distinguish themselves through small-batch production, sourdough and long fermentation techniques, and a commitment to transparency in sourcing and production. Think crusty sourdough loaves, delicate pastries, and the aroma of freshly baked bread wafting through the air. This dedication to quality and craftsmanship draws customers seeking a superior product and a connection to the baker's process.
Examples of successful artisanal bakeries include:
- Tartine Bakery (San Francisco): Known for its naturally leavened bread and exquisite pastries, Tartine has become a benchmark for artisanal baking worldwide.
- Poilâne (Paris, internationally recognized sourdough): Famous for its signature sourdough bread, Poilâne has built a legacy of traditional baking spanning generations.
- Sullivan Street Bakery (New York City): This popular bakery highlights the beauty of simple, well-made bread using high-quality ingredients.
Why choose an artisanal bakery as a food business idea? This model deserves its place on the list due to the growing consumer preference for artisanal products and the potential for premium pricing. It allows you to build a loyal community around quality and offers multiple revenue streams, including retail sales, wholesale partnerships with restaurants and cafes, and even baking classes.
Pros:
- Premium pricing potential
- Strong differentiation from commercial bakeries
- Multiple revenue streams (retail, wholesale, cafés, classes)
- Growing consumer preference for artisanal products
- Ability to build a loyal community around quality
Cons:
- Labor-intensive production methods
- Early morning work schedules
- Specialized skills and training required
- Higher ingredient costs
- Short shelf life of products
Tips for Starting an Artisanal Bakery:
- Start with a signature item: What will be your bakery's claim to fame? A perfect croissant? An unparalleled sourdough? A unique local grain bread?
- Consider wholesale accounts: Supplementing retail sales with wholesale partnerships can provide a steady income stream.
- Develop efficient production scheduling: Maximize oven use and minimize waste with careful planning.
- Build a social media presence: Showcase your production process and the beauty of your handcrafted goods. Instagram is your friend!
- Offer baking classes: Share your passion and generate additional revenue by teaching others the art of artisanal baking.
Popularized by baking luminaries like Chad Robertson (Tartine Bakery) and Apollonia Poilâne (Poilâne Bakery), and fueled by shows like The Great British Bake Off, interest in quality baking is at an all-time high. This presents a fantastic opportunity for aspiring entrepreneurs to enter the market and carve out their niche.
6. Plant-Based Food Products
Looking for innovative food business ideas? The plant-based food sector is booming, offering exciting opportunities for entrepreneurs. This business model focuses on developing and selling food products made entirely from plants, catering to a diverse and growing market of vegans, vegetarians, flexitarians, and health-conscious consumers. From meat alternatives and dairy substitutes to plant-based snacks and complete meal solutions, this category offers a wide range of possibilities for those seeking to capitalize on evolving consumer preferences. This makes it a strong contender amongst other food business ideas.
How it Works:
A plant-based food business centers around creating delicious and nutritious food products without using any animal ingredients. This involves significant research and development into plant protein formulations, focusing on ingredients like soy, pea protein, lentils, mushrooms, and seaweed. The goal is to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of traditional animal-based products while using only plant-derived sources.
Features and Benefits:
- Innovation in plant protein formulations: Creating unique and appealing textures and flavors is key to success.
- Clean label focus: Using recognizable ingredients builds consumer trust and aligns with the desire for natural foods.
- Sustainability messaging: Emphasizing the environmental benefits of plant-based diets resonates with environmentally conscious consumers.
- Nutritional fortification: Matching or exceeding the nutritional value of animal products enhances the appeal to health-conscious consumers.
- Texture and flavor development: Replicating the sensory experience of traditional foods is crucial for attracting a wider audience.
Pros:
- Rapidly growing market segment: The demand for plant-based foods is exploding, creating significant market opportunities.
- Appeal across multiple consumer demographics: The target market extends beyond vegans and vegetarians to include flexitarians and those seeking healthier options.
- Potential for intellectual property protection: Innovative formulations and processes can be protected through patents, giving businesses a competitive edge.
- Alignment with sustainability and health trends: This business model taps into two major consumer trends, increasing its long-term viability.
- Premium pricing potential: Consumers are often willing to pay a premium for high-quality, plant-based alternatives.
Cons:
- Substantial R&D investment requirements: Developing appealing and nutritious plant-based products can be costly and time-consuming.
- Complex ingredient sourcing and processing: Working with plant-based ingredients can be challenging and require specialized equipment.
- Regulatory challenges with labeling and claims: Navigating regulations related to plant-based food labeling and health claims can be complex.
- High competition from large food corporations: Established food companies are entering the plant-based market, increasing competition.
- Consumer skepticism about taste and texture: Overcoming negative perceptions about the taste and texture of plant-based foods remains a challenge.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Beyond Meat: A pioneer in plant-based burgers, Beyond Meat has achieved widespread success with its meat alternative products.
- Oatly: Oatly has revolutionized the dairy aisle with its popular oat milk products.
- Miyoko's Creamery: This company produces artisanal plant-based cheese and butter, demonstrating the potential for premium plant-based products.
Actionable Tips for Aspiring Entrepreneurs:
- Focus on taste and texture as primary selling points: Delicious food is essential for attracting and retaining customers.
- Develop compelling origin stories around ingredients: Transparency and storytelling can build consumer trust and brand loyalty.
- Consider co-manufacturing to reduce initial capital costs: Partnering with existing manufacturers can help reduce startup expenses.
- Build partnerships with chefs and restaurants for validation: Collaborating with culinary professionals can enhance credibility and reach a wider audience.
- Target specific nutritional profiles that compete with animal products: Addressing specific nutritional needs can attract health-conscious consumers.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This business model is ideal for entrepreneurs passionate about food innovation, sustainability, and healthy living. If you are driven by the desire to create positive change in the food system and capitalize on a rapidly growing market, then a plant-based food business might be the perfect fit. The increasing consumer demand for healthier and more sustainable food options makes this a particularly timely and promising food business idea.
Popularized By:
- Ethan Brown (Beyond Meat founder)
- Miyoko Schinner (Miyoko's Creamery)
- Celebrity investors like Leonardo DiCaprio and Bill Gates
7. Specialty Food E-commerce
Looking for innovative food business ideas? Specialty food e-commerce might be the perfect recipe for success. This model involves selling curated, premium, hard-to-find, or artisanal food products online. It's a fantastic option for entrepreneurs passionate about unique food offerings and reaching a wider audience. This business model deserves its place on this list because it combines the growing demand for unique food experiences with the convenience and reach of online shopping.
How it Works:
A specialty food e-commerce business operates on a direct-to-consumer model, cutting out the middleman and allowing for a closer relationship with customers. You source unique products, often directly from small-batch producers or artisans, and offer them through your online store. This can include everything from international ingredients and gourmet items to products catering to specific dietary needs like vegan, gluten-free, or keto. A key element is the curated nature of the selection; you're not just selling groceries, you're offering a carefully chosen collection that tells a story. Content marketing plays a crucial role, with recipes, blog posts, and educational materials highlighting the unique qualities of your products.
Examples of Success:
- Goldbelly: This platform partners with iconic restaurants across the country, allowing customers nationwide to order their signature dishes. (www.goldbelly.com)
- Mouth.com: Mouth.com focuses on curated American-made artisanal foods, offering a diverse selection of small-batch products. (www.mouth.com)
- Thrive Market: This membership-based platform offers natural and organic products, catering to health-conscious consumers. (www.thrivemarket.com)
Why Choose Specialty Food E-commerce?
This approach is ideal for entrepreneurs who are passionate about specific food niches and want to build a community around shared culinary interests. It's particularly attractive if you have an existing network of artisan producers or a deep understanding of a particular cuisine or dietary trend.
Features and Benefits:
- Curated Selection: Offer unique products not easily found elsewhere.
- Direct-to-Consumer Sales: Control the entire customer experience and build direct relationships.
- Content Marketing: Educate and engage customers with recipes, stories, and product information.
- Subscription Boxes: Generate recurring revenue and build customer loyalty.
- Community Building: Foster a sense of belonging among customers with shared food interests.
Pros:
- Lower startup costs compared to brick-and-mortar stores.
- Geographic reach beyond local markets.
- Data collection for personalized marketing.
- Scalable inventory management.
- Potential for high margins on exclusive products.
Cons:
- Perishability and shipping challenges.
- High customer acquisition costs.
- Inventory management complexities.
- Seasonal demand fluctuations.
- Competition from larger platforms like Amazon.
Actionable Tips:
- Develop a clear niche: Focus on a specific type of food, cuisine, or dietary restriction. Don't try to be everything to everyone.
- Create compelling content: Educate customers about your products and their origins. Share recipes and cooking tips.
- Build relationships with small producers: Secure exclusive offerings and support local businesses.
- Invest in quality packaging and temperature-control solutions: Ensure product freshness and safety during shipping.
- Implement a robust inventory management system: Track stock levels, manage orders, and prevent spoilage.
Popularized By:
Entrepreneurs like Joe Ariel (Goldbelly founder), Nick Taranto and Josh Hix (Plated founders), and various food influencers promoting specialty ingredients have significantly contributed to the popularity of this business model. This demonstrates the potential for success within the specialty food e-commerce space.
8. Fermented Food Production
Looking for food business ideas that tap into growing health trends? Fermented food production could be your niche. This business model revolves around creating naturally preserved foods using fermentation, a process that not only enhances flavors and extends shelf life but also creates beneficial probiotics. This makes it a particularly attractive option among current food business ideas.
Fermentation works by introducing beneficial microorganisms (like bacteria or yeasts) to food. These microbes consume sugars and starches, producing lactic acid, acetic acid, or alcohol. This process preserves the food, creates unique tangy flavors, and enriches it with probiotics, which are beneficial for gut health. Products in this category include kombucha, kimchi, sauerkraut, pickles, miso, tempeh, and artisanal vinegars. This aligns perfectly with the increasing consumer interest in gut health and traditional, natural food preservation methods, making fermented foods a strong contender among various food business ideas.
Successful examples of fermented food businesses include GT's Living Foods, a pioneer in the kombucha market, Farmhouse Culture, known for its organic kraut and gut shots, and Wildbrine, offering a variety of kimchi and fermented vegetables. These businesses demonstrate the potential for growth and profitability within this niche.
Why choose this food business idea? Fermented food production offers several advantages:
- Alignment with Health and Wellness Trends: The growing awareness of gut health and the benefits of probiotics creates a strong market demand for fermented foods.
- Extended Product Shelf Life: Fermentation naturally preserves food, reducing spoilage and extending its time on the shelves.
- Value-Added Transformation: Simple, inexpensive ingredients are transformed into high-value, sought-after products.
- Scalability: You can start small with minimal equipment and gradually scale up as your business grows.
- Strong Storytelling Potential: The history and cultural significance of fermented foods offer compelling marketing narratives.
However, there are also challenges to consider:
- Food Safety and Regulations: Strict adherence to food safety regulations and meticulous quality control are crucial when working with live cultures.
- Production Space: You'll need a dedicated space with appropriate temperature control and ventilation.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality with live cultures can be challenging.
- Consumer Education: Many consumers are unfamiliar with the taste and benefits of some fermented foods, requiring educational marketing efforts.
- Packaging: Special packaging may be necessary to accommodate active fermentation and maintain product quality.
Tips for Starting a Fermented Food Business:
- Small Batch Production: Start small to perfect your recipes and processes before scaling up.
- Supplier Relationships: Develop strong relationships with organic produce suppliers to ensure high-quality ingredients.
- Invest in pH Testing Equipment: Accurate pH measurement is essential for food safety.
- Educational Marketing: Focus on educating consumers about the health benefits and unique flavors of your products.
- Distribution: Consider refrigerated distribution networks early in your planning.
Figures like GT Dave (GT's Kombucha founder) and Sandor Katz (fermentation author and educator), along with numerous health influencers, have popularized fermented foods. Their influence, combined with increased consumer interest in healthy eating, makes this a promising area for aspiring food entrepreneurs. If you're seeking food business ideas with significant growth potential and a positive impact on consumer health, fermented food production is definitely worth exploring.
9. Cooking Classes and Culinary Experiences
Looking for food business ideas that are less capital-intensive than opening a restaurant but still tap into the booming culinary scene? Cooking classes and culinary experiences offer a fantastic way to share your passion for food and build a profitable business. This approach focuses on providing educational and interactive food-related activities, making it an experience-focused, rather than product-focused, food business idea.
Instead of selling dishes directly, you're selling knowledge, skills, and memorable moments. This could involve anything from teaching fundamental knife skills and sauce preparation to hosting themed workshops on pasta making, sushi rolling, or exploring regional cuisines. The format is incredibly versatile, allowing you to cater to various skill levels, from beginner cooks to seasoned foodies. You can also offer specialized classes like wine pairings, food photography for social media, or even foraging for edible plants.
How it Works:
Cooking classes and culinary experiences can be offered in a variety of settings, both virtual and in-person. You can host classes in your own kitchen, rent a commercial kitchen space, partner with existing venues like community centers, or even travel to your customers' homes. Online classes via platforms like Zoom have also become incredibly popular, expanding your potential reach far beyond your local area.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Sur La Table: This national retailer offers a wide range of in-person cooking classes across the country, demonstrating the scalability of this business model.
- The League of Kitchens: This organization offers immersive cooking workshops led by immigrant women in their own homes, showcasing the power of cultural culinary experiences.
- Airbnb Experiences: This platform features numerous cooking experiences hosted by locals around the world, highlighting the growing demand for unique and authentic food-related activities.
Why This Deserves a Spot on the List:
This food business idea offers a unique blend of creativity, education, and entrepreneurship. Its relatively lower startup costs compared to traditional food businesses like restaurants, coupled with multiple revenue streams (classes, private events, corporate team-building), make it a compelling option for aspiring food entrepreneurs. The high perceived value of experiential offerings allows for premium pricing, and there's the added opportunity to sell complementary products like aprons, cookbooks, or ingredient kits.
Features and Benefits:
- Interactive Learning Environments: Hands-on learning makes the experience engaging and memorable.
- Expertise-Based Instruction: Your culinary knowledge and passion are the core of this business.
- Customizable for Different Skill Levels and Interests: You can tailor your offerings to appeal to a broader audience.
- Virtual and In-person Delivery Options: Flexibility to reach more customers and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Flexible Scaling Options: Start small and grow as your business develops.
Pros:
- Lower startup costs than product-based food businesses.
- Multiple revenue streams (classes, events, corporate, private).
- High perceived value for experiential offerings.
- Opportunity to sell complementary products.
- Flexible scaling options.
Cons:
- Instructor knowledge and teaching ability are crucial.
- Scheduling and capacity limitations can be challenging.
- Seasonal demand fluctuations may impact revenue.
- Equipment and facility needs vary depending on the format.
- Marketing efforts are necessary to maintain consistent attendance.
Actionable Tips:
- Develop signature classes: Differentiate yourself from competitors with unique and specialized offerings.
- Partner with complementary businesses: Cross-promote with local wineries, farmers markets, or kitchen supply stores.
- Create pricing tiers: Offer different levels of experiences at varying price points.
- Build an email list: Stay connected with your audience and promote repeat bookings and special events.
- Target corporate team-building: This can be a lucrative segment for cooking class businesses.
Popularized By:
The rise of celebrity chef masterclasses, the success of initiatives like The League of Kitchens (founded by Lisa Gross), and the ongoing food tourism trend have all contributed to the popularity of cooking classes and culinary experiences.
This business model allows you to turn your culinary passion into a thriving enterprise while providing valuable and enjoyable experiences for your customers. It's a delicious slice of the food business pie that's ripe for innovation and growth.
Top 9 Food Business Ideas Comparison
| Business Idea | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 💡 Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | ⚡ Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Truck Business | Medium – regulatory hurdles and maintenance | Moderate – vehicle, equipment, permits | Moderate – break-even in 6-18 months | Urban centers, events, festivals, business districts | Mobile flexibility, lower startup than restaurants |
| Meal Prep Service | Medium – food safety and delivery logistics | Low to Moderate – kitchen facilities, packaging | High – recurring revenue, break-even in 8-14 months | Health-conscious, busy professionals, dietary-specific | Subscription model, scalable, diet specialization |
| Specialty Coffee Shop | High – equipment investment and skilled staff | High – equipment, trained baristas, location | High – 2-3 year break-even, loyal customer base | Urban coffee culture, artisanal product lovers | High margins, strong brand loyalty |
| Virtual Kitchen/Ghost Restaurant | Medium – dependency on delivery platforms | Moderate – commercial kitchen, digital branding | High – break-even in 6-12 months, multiple brand testing | Delivery networks, flexible menu concepts | Low overhead, quick concept pivots |
| Artisanal Bakery | High – labor-intensive, skill-based | High – specialized equipment, quality ingredients | Moderate – 12-24 months to break-even | Local markets, quality-focused consumers | Premium pricing, multiple revenue streams |
| Plant-Based Food Products | High – R&D and regulatory complexity | High – ingredient sourcing, processing, innovation | High – 2-5 year break-even, growing market demand | Vegan/vegetarian consumers, health and sustainability markets | Rapid growth, sustainability alignment |
| Specialty Food E-commerce | Medium – inventory and shipping challenges | Low to Moderate – website, packaging, suppliers | Moderate – 12-18 months break-even | Niche food enthusiasts, gourmet shoppers | Wide reach, lower startup cost than retail |
| Fermented Food Production | Medium – food safety and quality control | Low to Moderate – small batch equipment, fermentation space | Moderate – 12-24 months break-even | Health and wellness consumers, probiotic interest | Health focus, value-added traditional products |
| Cooking Classes and Culinary Experiences | Low to Medium – scheduling and instructor quality | Low – equipment, space, knowledge | Moderate – break-even in 6-12 months | Food enthusiasts, corporate events, experiential learners | Low startup, multiple revenue streams |
Ready to Cook Up Your Food Business Success?
From food trucks and meal prep services to virtual kitchens and artisanal bakeries, the culinary world is brimming with exciting food business ideas. We've explored nine diverse concepts, each offering a unique path to entrepreneurial success. Remember, the key takeaways are thorough market research, a well-defined business plan, and an unwavering commitment to quality. Mastering these elements is vital for navigating the competitive food industry and building a sustainable, profitable business. Whether you're drawn to the fast-paced energy of a food truck or the creative freedom of a specialty food e-commerce store, the right food business idea can transform your passion into a thriving enterprise.
By understanding the nuances of each model—from plant-based food production to fermented food trends and even the immersive world of cooking classes—you can identify the perfect opportunity to satisfy market demand and achieve your entrepreneurial goals. Launching a food business is more than just crafting delicious dishes; it's about building a brand, fostering customer loyalty, and ultimately, sharing your culinary vision with the world.
Ready to transform your food business ideas into reality? Explore the comprehensive resources available at Business Ideas DB to refine your concept, analyze market trends, and gain the insights you need to launch and grow your culinary venture. Let Business Ideas DB be your trusted partner in navigating the exciting world of food entrepreneurship.
Explore More Ideas
Want more ideas like this? Check out Business Ideas DB for consumer app ideas backed by market research.
Explore Ideas